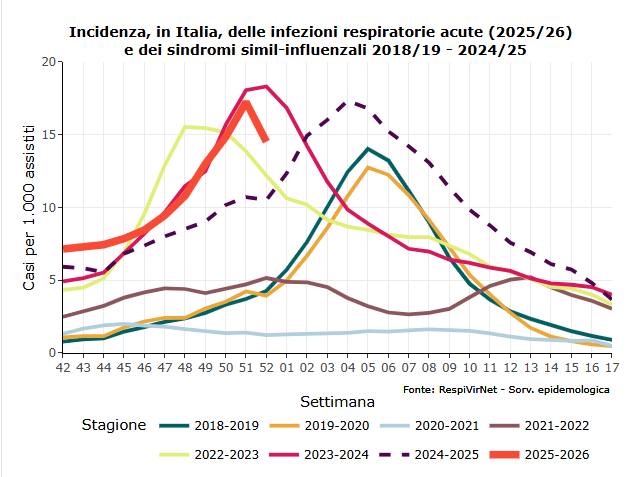
ROMA (ITALPRESS) – The total incidence of acute respiratory infections in the community, in the week from 22 to 28 December, was equal to 14,5 cases per 1,000 assisted, decreasing compared to the previous week, when it was 17,1. This is what emerges from the report of RespiVirNet surveillance, published today by the Higher Institute of Health and this year in an interactive form. The data reported this week, in particular those coming from sentinel surveillance in the community, may not reflect the real incidence and circulation of influenza viruses due to a possible reduction in the number of visits and data transmitted in conjunction with Christmas holidays. The decline could also be attributed to the closure of schools, which every year results in a small decline in the seasonal trend. The suspension of school activities reduces the transmission of respiratory viruses in age groups where circulation is more intense. Approximately 820 thousand new cases have been estimated, with a total of about 6.7 million cases from the start of surveillance. The highest incidence is observed, as usual, in the age range 0-4 years, with about 39 cases per 1,000 assisted.
“The decline recorded this week could be attributable to minor reports made by family doctors on Christmas week, as evidenced by the fact that the decline is more evident in the data from communities than the hospital flow, and also the closure of schools – comment ISS experts from the ISS department of Infectious Diseases of Iss -. The incidence could then go back up, or still stay high even in the coming weeks.” The intensity is very high in Sicily, high in Campania, average in Piedmont, Emilia Romagna, Tuscany, Marche, Lazio, Abruzzo, Umbria and Puglia, while it is low in all the others. The change in the definition of case from ILI to ARI makes it difficult to compare the weekly incidence with that of the previous seasons, as well as with the thresholds of intensity, calculated on the basis of the data relating to the symil-fluid syndromes of the last seasons. In the week both in the community and in the hospital flow there is a high rate of positivity in people with respiratory infections, especially in hospitals (22.2% and 50.3% respectively). Surveillance of serious and complicated forms of influence shows an increase in the number of cases in week 51 (corresponding to the period 16-22 December, last consolidated data) compared to the same week of the previous season. The most prevalent subtype of severe forms is A(H3N2). It is reported that most cases of serious influence and with complications concern unvaccinated people.
With regard to the characterization of influenza viruses, in the community the percentage of A(H3N2) virus is far greater than the A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses. In the hospital flow there is also a higher percentage of A(H3N2) virus than that of A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses. To date no sample has been positive for type A influence “not subtipizzabile” as a seasonal influence, which could be indicative of the circulation of aviarian strains. Sequential analysis in progress from the beginning of the surveillance show that among the fluent virus strains A H3N2 currently circulating in Italy the subclade K is clearly prevalent, while between the strains H1N1 pdm09, all strains are grouped exclusively in the subclade D.3.1 within the broadest clade 5a.2a.1 to which also belong vaccinal strains.
– graphic photo ISS –
(ITALPRESS).